The economy of Bangladesh is constituted by that of a developing country. Its per capita income in 2008 was US$1389 lower than the world average of $10,497. According to the gradation by the International Monetary Fund, Bangladesh ranked as the 48th largest economy in the world in 2008, with a gross domestic product of US$224,889 million. The economy has grown at the rate of 6-7% p.a. over the past few years. While more than half of the GDP belongs to the service sector, more than 60% people of Bangladeshis are employed in the agriculture sector.
Remittances from Bangladeshis working overseas, mainly in the Middle East and East Asia, as well as exports of garments is the main source of foreign exchange earning.
The land is devoted mainly to rice and jute cultivation, although wheat production has increased in recent years; the country is largely self-sufficient in rice production.
Although improving at a very fast rate, infrastructure to support transportation, communications, power supply and water distribution is slowly developed. Bangladesh is limited in its reserves of oil, but recently there was huge development in coal mining. While the service sector has expanded rapidly during last two decades, country’s industrial base remains narrow. The country’s main endowments include its vast human resource base, rich agricultural land, relatively abundant water, and substantial reserves of natural gas which are depleting quickly.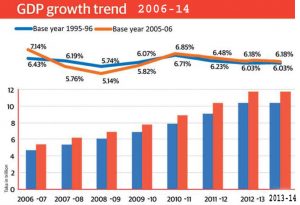
Agriculture
Agriculture is the single largest producing sector of Bangladesh economy since it comprises about 30% of the country’s GDP and employs mare than 60% of the total labour force. Most Bangladeshis earn their living from agriculture. Rice is Bangladesh’s principal crop. Jute was considering golden fibre of Bangladesh but now a days getting less inportance to produce and wheat is assuming greater importance. Tea is grown in the northeast hilly areas. Because of Bangladesh’s fertile soil and normally ample water supply, rice can be grown and harvested three times a year in many areas. Due to a number of factors, Bangladesh’s labor-intensive agriculture has achieved steady increases in food grain production despite the often unfavorable weather conditions. These include better flood control and irrigation, a generally more efficient use of fertilizers, and the establishment of better distribution and rural credit networks.
Textile sector & Industry
Many new jobs – mostly for women – have been created by the country’s dynamic private ready-made garment industry. Bangladesh’s textile industry, which includes knitwear and ready-made garments along with specialized textile products, is the nation’s number one export earner. The sector, which employs 2.2 million workers, accounted for 75 per cent of Bangladesh’s total exports of US$10.53 billion in FY2005-06, in the process logging a record growth rate of 24.44 per cent.
Other industries which have shown very strong growth include the chemical industry, steel industry, mining industry and the paper and pulp industry.
Economy Overview of Bangladesh
Currency Bangladesh Taka (BDT)
Fiscal year 1 July – 30 June
Trade organizations WTO, SAFTA, D8, WCO
GDP $228.4 billion (2008 est.PPP)
GDP growth 6.5% (2008 est.)
GDP per capita $ 1500 (2008 est.PPP)
GDP by sector Agriculture (19%), industry (28.7%), services (53.7%) (2007 est.)
Inflation (CPI) 9.4% (2008 est.)
Population below poverty line 38% (2009 est.)
Labour force 70.86 million (2008 est.)
Labour force by occupation Agriculture (65%), industry (25%), services (10%) (2005 est.)
Unemployment 2.4% (2008)
Main industries jute manufacturing, cotton textiles, garments, tea processing, paper newsprint, sugar, light engineering, chemical, cement, fertilizer, food processing
External
Exports $16.298 billion (2009)
Export goods garments, jute and jute goods, leather, frozen fish and seafood
Main export partners US 31.8%, Germany 10.9%, UK 7.9%, France 5.2%, Netherlands 5.2%, Italy 4.42% (2000)
Imports $25.205 billion (2008)
Import goods machinery and equipment, chemicals, iron and steel, raw cotton, food, crude oil and petroleum products,
Main import partners India 10.5%, EU 9.5%, Japan 9.5%, Singapore 8.5%, China 7.4%(2004)
Gross External Debt $21.23 billion (31 December 2007 est.)
Public finances
Public Debt $1.2 billion (June 2005 est.)
Revenues $8 billion (2007 est.)
Expenses $11 billion (2007 est.)
Economic aid $1.575 billion (2000 est.)
Source: wikipedia